
Assessment of the digestive system malignancy information in Wikipedia and Baidu Encyclopedia: a longitudinal study
Introduction
In September 2021, the number of Internet users in the world reached 5.16 billion, of which China, as the most populous country in the world, accounts for 18.2% (940 million) (1,2). Due to the rise and rapid development of the Internet, its convenience, and the immense amount of information available, it has gradually become the main source from which people obtain information. A study found that 87.8% of scoliosis patients searched the Internet for health-related information (3), and >50% of United States Internet users search for Internet-based medical information (4,5). As these studies show, the Internet has become an important health-information source for patients. An increasing number of people search for disease information on the Internet, but the accuracy and reliability of this medical information has yet to be verified (6,7).
Wikipedia is a web-based encyclopedia that contains close to 6 million articles in English (8-10). It provides valuable disease information. Previous studies have compared search engines and shown that medical sources from Wikipedia are more reliable than others sources (9,11); however, online articles still contain more errors than peer-reviewed sources (12). Baidu Encyclopedia, China’s version of Wikipedia (13), publishes more than 16 million articles in Chinese. Wikipedia and Baidu Encyclopedia are the most wildly used English and Chinese search engine websites, respectively (14-16); however, the quality of the medical information contained on these websites has not yet been examined.
Malignancies originating from digestive system are the common malignant tumors in human beings. This study sought to evaluate the quality and timeliness of medical information related to digestive system malignancy retrieved from Wikipedia and Baidu Encyclopedia. Due to the high frequency of updates on the Internet, we were of the view that 3 years could be used as an extended period to assess changes in the information over a long interval. A longitudinal study is one that repeats the same or same group of subjects over a relatively long period of time. We monitored Wikipedia and Baidu Encyclopedia over a 3-year period to compare whether the information on these search engines improved over that time. Our findings will help people determine the reliability of online encyclopedia entries, and help patients to avoid medical issues that could arise if they rely on unreliable information on the websites.
Methods
Data sources
The articles involved in this study were all obtained from Wikipedia (8) and Baidu Encyclopedia (13). For the 3-year follow-up period, the initial data collection period ran from June 20, 2019 to July 1, 2019, and the final data collection period ran from June 20, 2022 to July 1, 2022. A period of 3 years is an acceptable and widely used length for a follow-up period (17-19); thus, we chose 3 years as the follow-up time for the comparison.
Retrieval of liver disease articles
The International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (10th revision, version 2016; ICD-10) is the diagnostic classification criteria for all clinical and research purposes. The ICD sets uniform diagnostic and classification criteria for all health-related diseases. In the ICD-10, digestive system malignancy (i.e., malignant neoplasms of digestive organs) are classified as neoplasms in Chapter II, with categories ranging from C15 to C26 (20). Based on the diagnostic and classification codes provided by the ICD-10, this study investigated articles and entries on Wikipedia and Baidu Encyclopedia. All the ICD-10 classification code titles for the malignant neoplasms of digestive organs were used for the retrieval. Entries without search results were excluded from the study. Search terms on these websites are listed in Tables S1-S4, respectively. A proportion of the available search results was recorded and analyzed.
Assessment of the quality of the research articles
The DISCERN instrument, which is a tool for judging the quality of health information on treatment choices, was used to assess the quality of the articles retrieved from Wikipedia and Baidu Encyclopedia (21); however, its actual function is a matter of debate. Some scholars have argued that the original version of the DISCERN instrument is not suitable for evaluating Wikipedia articles (22,23); however, a great deal of recent research has still used the DISCERN instrument to evaluate the quality of online Wikipedia articles (15,16). Thus, in the absence of a better tool, the DISCERN instrument was considered an appropriate tool for evaluating the quality of the Wikipedia online articles.
The DISCERN instrument comprises 16 questions that are rated on a 5-point scale (on which 1 = definitely no, and 5 = definitely yes). The testable questions are divided into 3 sections. Section 1 (Questions 1 to 8) assesses the reliability of a paper, Section 2 (Questions 9 to 15) focuses on the quality of the treatment information, and Section 3 (question 16) evaluates the overall quality of the articles (21). The higher DISCERN score, the better the quality of the article. Overall, a total DISCERN score can range from 16 to 80, and based on the total score, the articles are categorized as very poor (a score of 16–26), poor (a score of 27–38), fair (a score of 39–50), good (a score of 51–62), and excellent (a score of 63–80) (15,16).
In this study, 4 authors evaluated the quality of the articles. All of the authors were surgeons specializing in general surgery with years of practice experience. They were capable of professionally evaluating the medical-related information provided in the articles retrieved from Wikipedia and Baidu Encyclopedia. Of the 4 authors, 3 used the DISCERN instrument to evaluate the articles retrieved from Baidu Encyclopedia and Wikipedia. The discrimination scores were determined by discussion, after which, all the authors agreed on the final score. If a consensus was unable to be reached during the discussion, the 4th author, who was the most senior, made the final determination.
Timeliness of the updated articles
We planned to assess the timeliness of the articles by analyzing the time interval between updates, which reflects the update frequency of the webpages. The update interval was calculated as the date interval between the update date and the date on which we performed the search. In 2019, the update interval was calculated as the interval between the updated date and July 1, 2019. In 2022, the update interval was calculated as the date interval between the updated date and July 1, 2022. We compared the update interval of each article to evaluate the update timeliness of the article retrieved from Wikipedia or Baidu Encyclopedia.
Statistical analysis
SPSS software (version 26.0) was used for the statistical analysis. The samples with a normal distribution were analyzed by an independent sample t-test and a Welch correction or a paired sample t-test. The samples without a normal distribution were analyzed using a non-parametric test. A P value <0.05 was considered statistically significant. GraphPad Prism version 9 software (GraphPad Prism Software Inc) was used for figure production and rendering.
Results
Retrieval of liver disease articles
Malignant neoplasms of digestive organs are classified as Chapter II in ICD-10 (version 2016). They are divided into 12 categories (C15–C26) according to the pathogenic sites or organs, and there is a total of 109 disease items. Through the search, only a portion of the disease items could be retrieved in relevant article, while some other items may be retrieved to more than one relevant article. We included all these relevant articles in this study.
In 2019 and 2022, we retrieved a total of 50 and 52 articles, respectively, from Baidu Encyclopedia, representing an increase of 2 articles and no deleted articles, and 30 and 31 articles, respectively from Wikipedia, representing an increase of 1 article and no deleted articles (see Table 1). In terms of quantity, the number of articles on both websites increased, and more articles were retrieved from Baidu Encyclopedia than Wikipedia.
Table 1
| ICD-10 category | Articles included in the ICD-10 classification (n=109) | Baidu Encyclopedia articles in 2019 (n=50) | Wikipedia articles in 2019 (n=30) | Baidu Encyclopedia articles in 2022 (n=52) | Wikipedia articles in 2022 (n=31) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C15 malignant neoplasm of esophagus | 9 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| C16 malignant neoplasm of stomach | 22 | 10 | 3 | 11 | 3 |
| C17 malignant neoplasm of small intestine | 6 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
| C18 malignant neoplasm of colon | 16 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 1 |
| C19 malignant neoplasm of rectosigmoid junction | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| C20 malignant neoplasm of rectum | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| C21 malignant neoplasm of anus and anal canal | 8 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| C22 malignant neoplasm of liver and intrahepatic bile ducts | 12 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 7 |
| C23 malignant neoplasm of gallbladder | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| C24 malignant neoplasm of other and unspecified parts of biliary tract | 12 | 5 | 2 | 5 | 2 |
| C25 malignant neoplasm of pancreas | 15 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| C26 malignant neoplasm of other and ill-defined digestive organs | 4 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
ICD-10, International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision.
Evaluation of the quality of articles
In the absence of any better evaluation tool, the DISCERN instrument was used to score the articles included in this study. According to the design features of the DISCERN instrument, 3 scores can be obtained for Sections 1, 2, and 3, and the total score is calculated by summing up the scores for each section (see Figure 1). In the horizontal comparison, the score of Wikipedia in Section 1 was significantly higher than that of Baidu Encyclopedia in both 2019 and 2022, and the difference was statistically significant (19.07±0.90 vs. 15.24±0.62, P<0.001 in 2019; 19.65±0.99 vs. 15.87±0.67, P<0.0001 in 2022, respectively). In Sections 2 and 3, there were no significant statistically significant differences between Wikipedia and Baidu Encyclopedia in 2019 or 2022. Overall, Wikipedia’s total scores were significantly higher than Baidu Encyclopedia’s total scores in 2019 and 2022, and the difference was statistically significant (34.03±1.99 vs. 28.38±1.11, P=0.02 in 2019; 35.42±2.19 vs. 29.5±1.26, P=0.003 in 2022, respectively) (see Table 2). Thus, the quality of articles from Wikipedia was better than the quality of articles from Baidu Encyclopedia in 2019 and 2022.
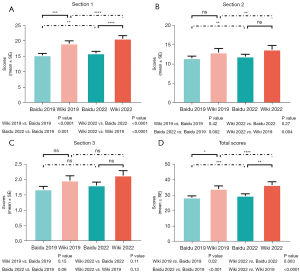
Table 2
| Year, sections of DISCERN | Baidu Encyclopedia, mean ± SE | Wikipedia, mean ± SE | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | |||
| Section 1 | 15.24±0.62 | 19.07±0.90 | <0.001 |
| Section 2 | 11.46±0.55 | 12.93±1.06 | 0.42 |
| Section 3 | 1.68±0.10 | 2.03±0.16 | 0.15 |
| Total score | 28.38±1.11 | 34.03±1.99 | 0.02 |
| 2022 | |||
| Section 1 | 15.87±0.67 | 19.65±0.99 | <0.0001 |
| Section 2 | 11.88±0.62 | 13.45±1.13 | 0.27 |
| Section 3 | 1.75±0.10 | 2.32±0.20 | 0.11 |
| Total score | 29.5±1.26 | 35.42±2.19 | 0.003 |
SE, standard error.
We classified the included articles according to their DISCERN scores. Among the articles from Baidu Encyclopedia, 6 articles were evaluated to be of fair quality, 23 of poor quality, and 21 of very poor quality in 2019, while 9 articles were evaluated to be of fair quality, 21 of poor quality, and 22 of very poor quality in 2022. Among the articles from Wikipedia, 4 articles were evaluated to be of good quality, 5 of fair quality, 13 of poor quality, and 8 of very poor quality in 2019, while 5 articles were evaluated to be good quality, 5 of fair quality, 13 of poor quality, and 8 of very poor quality in 2022. Thus, a vertical comparison was performed to find out whether the quality of the articles on the 2 websites improved over the 3-year period of updates. The Section 1 score in 2022 was significantly higher than that in 2019 for both websites, and the difference was statistically significant (15.87±0.67 vs. 15.24±0.62, P=0.001 in Baidu Encyclopedia; 19.65±0.99 vs. 19.07±0.90, P<0.0001 in Wikipedia). The results for the Section 2 scores were similar (11.88±0.62 vs. 11.46±0.55, P=0.002 in Baidu Encyclopedia; 13.45±1.13 vs. 12.93±1.06, P=0.004 in Wikipedia, respectively). In relation to the Section 3 score, there was no statistically significant difference between 2019 and 2022. Overall, the total score in 2022 was significantly higher than that in 2019, and the difference was statistically significant (29.5±1.26 vs. 28.38±1.11, P<0.001 in Baidu Encyclopedia; 35.42±2.19 vs. 34.03±1.99, P<0.0001 in Wikipedia) (see Table 3).
Table 3
| Websites, sections of DISCERN | 2019, mean ± SE | 2022, mean ± SE | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baidu Encyclopedia | |||
| Section 1 | 15.24±0.62 | 15.87±0.67 | 0.001 |
| Section 2 | 11.46±0.55 | 11.88±0.62 | 0.002 |
| Section 3 | 1.68±0.10 | 1.75±0.10 | 0.06 |
| Total score | 28.38±1.11 | 29.5±1.26 | <0.001 |
| Wikipedia | |||
| Section 1 | 19.07±0.90 | 19.65±0.99 | <0.0001 |
| Section 2 | 12.93±1.06 | 13.45±1.13 | 0.004 |
| Section 3 | 2.03±0.16 | 2.32±0.20 | 0.13 |
| Total score | 34.03±1.99 | 35.42±2.19 | <0.0001 |
SE, standard error.
Timeliness of articles
The time interval between updates represents the timeliness of the article. To compare the timeliness of the articles from Baidu Encyclopedia and Wikipedia, we recorded and followed up the update intervals of the 2 websites in 2019 and 2022 (see Figure 2). In 2019, the mean update interval for Baidu Encyclopedia articles was 970.88 days, while the mean update interval for Wikipedia articles was 100.23 days. The update interval for articles in Baidu Encyclopedia was significantly longer than the update interval for articles in Wikipedia, and the difference was statistically significant (970.88±91.05 vs. 100.23±24.90, P<0.0001). In 2022, the mean update interval for Baidu Encyclopedia articles was 1,280.05 days, while the mean update interval for Wikipedia articles was 54.61 days. The update interval for articles in Baidu Encyclopedia was significantly longer than that for articles in Wikipedia, and the difference was statistically significant (1,280.05±119.10 vs. 54.61±7.76, P<0.0001). The update interval for Baidu Encyclopedia was significantly longer than that for Wikipedia, which means that the articles on Wikipedia were more timely. However, the update interval for Baidu Encyclopedia in 2022 was shorter than that in 2019 (1,280.05±119.10 vs. 970.88±91.05, P=0.002). Thus, after 3 years of follow-up, the timeliness of the Baidu Encyclopedia articles had improved.

Discussion
With the rapid development of technology and science, the Internet has gradually become the most common way for people to search for information. An increasing number of people search for relevant information or even treatment plans on the Internet when they have health problems (5). However, issues arise because the information that the networks provide is uninspected (6). Indeed, previous research has shown that the health information provided by search engines is not credible (24-26). We conducted this study to assess the quality of medical-related information provided to people by Baidu Encyclopedia and Wikipedia, the 2 most popular and widely accessible search engines in Chinese and English, respectively (9). As malignant tumors of the digestive tract are a threat to people’s health (27), and the incidence of such tumors has been on the rise in recent years, we took these tumors as the object of the disease evaluation. We analyzed the quality and improvement of articles on the 2 websites before and after the 3-year follow-up, and also compared the update intervals of the articles over the 3-year period to determine the timeliness of the websites. The results were not satisfactory. Wikipedia had a higher quality of articles than Baidu Encyclopedia; however, most of the articles were of low quality.
The DISCERN instrument contains 3 sections (see Figure 1). Section 1 mainly evaluates whether the information contained in an article is reliable and has a clear source. Wikipedia is a good search engine for medical information on the internet (9,14) and is a much more detailed source of information than Baidu Encyclopedia. The sources (e.g., books, literature, or websites) of the data mentioned in most articles, such as morbidity and mortality data, are tagged in most articles. In Wikipedia, the citations can be clearly identified and can be directly linked to a corresponding academic database, such as PubMed. High-quality references guarantee the reliability of an article (28). Over the 3 years of the updates, both websites improved in this area.
Section 2 focuses on the quality of information on treatment choices. In many of the articles we retrieved, treatment was only vaguely mentioned or not mentioned at all. For oncological diseases, most articles only described surgical treatment, and there were few references to radiotherapy, chemotherapy, or targeted therapy. However, studies have shown that for gastrointestinal tumors, chemoradiotherapy is also an effective treatment (29). For liver cancer, in addition to surgery, transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is also a possible option. Beyond that, chemotherapy drugs, such as sorafenib and regorafenib, and programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) targeting drugs can be used as treatments (30). Such omissions will seriously affect patients’ understanding of the treatment of diseases, and may be misleading and may even cause conflicts between doctors and patients (31). Both websites scored low on this section, but both had improved after the 3-year follow-up period.
Section 3 provides a general evaluation of the article. No difference was found in the scores of the 2 websites, which were both low. Additionally, the 2 websites showed no significant improvement over time. Wikipedia scored higher in all 3 sections and the total score, indicating that articles from Wikipedia were of higher quality than those from Baidu Encyclopedia. The articles on both websites improved the standardization of the data cited, and the quality of the treatment choices, which is of most concern to patients. The total scores had increased; however, the scores remained low, and the reliability of the articles were still not ideal.
During the search process, we also found that the Wikipedia articles were illustrated by a large number of accurate pictures. Some of the images could even be considered specialist and might be difficult for non-medical readers to understand. Additionally, Wikipedia is not a dependable source for medical students (22,32). Conversely, Baidu Encyclopedia articles had few illustrations, and while most were easy to understand, the accuracy was relatively poor, and many of the pictures were old.
Wikipedia’s information framework is very clear, and similar search terms are combined. A table or tree diagram is designed for a class of diseases with jump links for related entries (33,34). Such features increase the readability of articles. Baidu Encyclopedia had many similar entries, some of which refer to different Chinese names for the same disease. Thus, the Baidu Encyclopedia articles were repetitive, and this may also explain why Baidu Encyclopedia had a larger number of articles than Wikipedia. The website interface of Wikipedia is concise and clear, while keywords in Baidu Encyclopedia will be highlighted in the texts. Both search engines have their own advantages.
Over the course of 3 years, we found that Wikipedia updates its articles quite frequently, even several times a day. Some of these updates reflected modifications to the latest guidelines, and some were corrections to words or even spelling and grammar. Baidu Encyclopedia did a poor job in updating information, and some articles were not updated at all during the entire follow-up period.
Websites such as Baidu Encyclopedia and Wikipedia have a wide audience. Information provided to the general public should not be riddled with errors or irregularities. Patients’ therapeutic effect and prognosis will be affected by the wrong information. Unfortunately, as noted above, inaccuracies in expression, irregular citations, and a lack of treatment-related advice are widespread. The Internet is not yet a reliable source of medical information. In order to reduce the negative impact of inaccurate information in Wikipedia and Baidu Encyclopedia, website maintainers should update and correct articles in a timely manner. The professional qualifications of the authors of the articles should be more strictly checked. To improve this situation, we suggest that the websites establish a strict review process for professional articles and tighten the qualification process for article authors. More professionals need to be recruited to participate in the writing of professional articles. Baidu Encyclopedia launched the rainbow project on December 9, 2012, and since then, all medical online entries can only be edited and revised by certified medical personnel. This has increased the quality of the provided health information (35). Active references to progressive diagnosis and treatment plans or guidelines are also urgently needed. Regular updates should be provided to ensure the timeliness of the articles. Further, individual differences were found in the occurrence and development of the disease in each patient; thus, the Internet cannot replace clinicians. Reliable professional advice should be sought directly from medical personnel (36). We hope that in the future, hospitals will not only be responsible for treating people when they become ill, but will also be responsible for providing accurate and accessible health education to the public before illness occurs.
This study had some limitations. First, digestive tract malignancies are only one of the many diseases that threaten human health, and thus are not fully representative of all types of diseases. Second, in the study of the update time interval, the selection of different time nodes may have affected the analysis. The results need to be verified by more follow-up studies. Third, it is still controversial as to whether the DISCERN instrument can be used as an effective evaluation method. Better evaluation tools are needed that are recognized by the public for future studies.
In conclusion, the quality and timeliness of articles on gastrointestinal malignancies on Wikipedia are better than those on Baidu Encyclopedia. The quality of articles on both Baidu Encyclopedia and Wikipedia articles have improved over the past 3 years. However, there is still no guarantee of the comprehensiveness or reliability of any treatment information obtained from the Internet. Thus, patients should consult a medical professional directly.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Jinbang Kou from Shandong Hi-Speed Sichuan Industrial Development Co., Ltd. for providing technical support.
Funding: This study was supported by the grant of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82270648) and the grant of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82203785).
Footnote
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://atm.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/atm-22-4435/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical Statement: The authors are accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Open Access Statement: This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), which permits the non-commercial replication and distribution of the article with the strict proviso that no changes or edits are made and the original work is properly cited (including links to both the formal publication through the relevant DOI and the license). See: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
References
- Internet World Stats. World Internet Users and 2022 Population Stats. Available online: http://www.internetworldstats.com/stats.htm (accessed 2022-06-27).
- CNNIC. The 46th China Statistical Report on Internet Development. Available online: http://www.cac.gov.cn/202009/29/c_1602939918747816.htm (accessed 2020-09-30).
- Bao H, Zhu F, Wang F, et al. Scoliosis related information on the internet in China: can patients benefit from this information? PLoS One 2015;10:e0118289. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Jin J, Yan X, Li Y, et al. How users adopt healthcare information: An empirical study of an online Q&A community. Int J Med Inform 2016;86:91-103. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Zhao Y, Zhang J. Consumer health information seeking in social media: a literature review. Health Info Libr J 2017;34:268-83. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Jo JH, Kim JR, Kim MJ, et al. Quality and readability of online information on dental treatment for snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. Int J Med Inform 2020;133:104000. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Baumann E, Czerwinski F, Reifegerste D. Gender-Specific Determinants and Patterns of Online Health Information Seeking: Results From a Representative German Health Survey. J Med Internet Res 2017;19:e92. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Wikipedia. Wikipedia. Available online: https://www.wikipedia.org/ (accessed 2022-07-01).
- Laurent MR, Vickers TJ. Seeking health information online: does Wikipedia matter? J Am Med Inform Assoc 2009;16:471-9. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Farič N, Potts HW. Motivations for contributing to health-related articles on Wikipedia: an interview study. J Med Internet Res 2014;16:e260. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Thomas GR, Eng L, de Wolff JF, et al. An evaluation of Wikipedia as a resource for patient education in nephrology. Semin Dial 2013;26:159-63. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Hasty RT, Garbalosa RC, Barbato VA, Valdes PJ Jr, Powers DW, Hernandez E, et al. Wikipedia vs. peer-reviewed medical literature for information about the 10 most costly medical conditions. J Am Osteopath Assoc 2014;114:368-73. [PubMed]
- Baidu. Baidu Encyclopedia. Available online: http://baike.baidu.com/ (accessed 2022-07-01).
- Weiner SS, Horbacewicz J, Rasberry L, et al. Improving the Quality of Consumer Health Information on Wikipedia: Case Series. J Med Internet Res 2019;21:e12450. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Yacob M, Lotfi S, Tang S, et al. Wikipedia in Vascular Surgery Medical Education: Comparative Study. JMIR Med Educ 2020;6:e18076. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Modiri O, Guha D, Alotaibi NM, et al. Readability and quality of wikipedia pages on neurosurgical topics. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2018;166:66-70. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Na X, Guo H, Zhang Y, et al. Mining Open Payments Data: Analysis of Industry Payments to Thoracic Surgeons From 2014-2016. J Med Internet Res 2018;20:e11655. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Musy SN, Endrich O, Leichtle AB, et al. Longitudinal Study of the Variation in Patient Turnover and Patient-to-Nurse Ratio: Descriptive Analysis of a Swiss University Hospital. J Med Internet Res 2020;22:e15554. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Jabaley CS, Groff RF, Barnes TJ, et al. Sepsis information-seeking behaviors via Wikipedia between 2015 and 2018: A mixed methods retrospective observational study. PLoS One 2019;14:e0221596. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- WHO. ICD-10 version: 2016. 2016. Available online: http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2016/en (accessed 2019-06-25).
- Charnock D, Shepperd S, Needham G, et al. DISCERN: an instrument for judging the quality of written consumer health information on treatment choices. J Epidemiol Community Health 1999;53:105-11. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Azer SA. Is Wikipedia a reliable learning resource for medical students? Evaluating respiratory topics. Adv Physiol Educ 2015;39:5-14. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Azer SA, AlSwaidan NM, Alshwairikh LA, et al. Accuracy and readability of cardiovascular entries on Wikipedia: are they reliable learning resources for medical students? BMJ Open 2015;5:e008187. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Prasanth AS, Jayarajah U, Mohanappirian R, et al. Assessment of the quality of patient-oriented information over internet on testicular cancer. BMC Cancer 2018;18:491. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Azer SA, Alghofaili MM, Alsultan RM, et al. Accuracy and Readability of Websites on Kidney and Bladder Cancers. J Cancer Educ 2018;33:926-44. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Zhu X, Qiu X, Wu D, et al. Reliability of information about the use of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy from three major web search engines in China. PLoS One 2018;13:e0208783. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Sonnenberg WR. Gastrointestinal Malignancies. Prim Care 2017;44:721-32. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Heilman JM, West AG. Wikipedia and medicine: quantifying readership, editors, and the significance of natural language. J Med Internet Res 2015;17:e62.
- Diamantis A, Bouliaris K, Christodoulidis G, et al. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors and synchronous intra-abdominal malignancies: Review of the literature. J BUON 2018;23:1573-9. [PubMed]
- Anwanwan D, Singh SK, Singh S, et al. Challenges in liver cancer and possible treatment approaches. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 2020;1873:188314. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Hahne J, Liang T, Khoshnood K, et al. Breaking bad news about cancer in China: Concerns and conflicts faced by doctors deciding whether to inform patients. Patient Educ Couns 2020;103:286-91. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Azer SA. Evaluation of gastroenterology and hepatology articles on Wikipedia: are they suitable as learning resources for medical students? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014;26:155-63. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Good BM, Clarke EL, Loguercio S, et al. Building a biomedical semantic network in Wikipedia with Semantic Wiki Links. Database (Oxford) 2012;2012:bar060. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Lamprecht D, Lerman K, Helic D, et al. How the structure of Wikipedia articles influences user navigation. New Rev Hypermedia Multimed 2017;23:29-50. [Crossref] [PubMed]
- Beijing Morning Post. Rainbow Plan. 2012 Dec 10. Available online: http://tech.qq.com/a/20121210/000054.htm (accessed 2022-07-22).
- Biggs TC, Jayakody N, Best K, et al. Quality of online otolaryngology health information. J Laryngol Otol 2018;132:560-3. [Crossref] [PubMed]
(English Language Editor: L. Huleatt)


